Web Performance Specifications
Navigation Timing - 2012
为了帮助开发者更好地衡量页面性能,W3C 在 2012 年提出了 Navigation Timing
该标准提供了 PerformanceTiming PerformanceNavigation 接口,通过只读属性的方式,提供了完整的客户端延迟度量 (complete client-side latency measurements),具体内容可以查看 MDN 或者 W3C Recommendation
标准细化的指标都存储在全局的 performance 上,可以直接通过 const {navigation, timing} = window.performance 的方式读取
为什么需要 Navigation Timing
假设有如下代码,旨在衡量页面的加载时间
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript">
var start = new Date().getTime();
function onLoad() {
var now = new Date().getTime();
var latency = now - start;
alert("page loading time: " + latency);
}
</script>
</head>
<body onload="onLoad()">
<!-- Main page body goes from here. -->
</body>
</html>实际上该脚本有一个明显的问题:它只会在 script 执行时才开始计算,而没有累计任何 从服务端获取页面 的时间
基于以上原因,W3C 基于页面的生命周期,在PerformanceTiming 和 NavigationTiming 中定义了包含了 navigationStart 在内的属性,方便衡量从前一个页面卸载开始的整个页面周期内页面加载耗时的各项指标
Navigation Timing 的处理模型
Performance Timing 以及 Navigation Timing 准确来讲并不是直接的衡量指标,而是基于页面周期的 时间点
如下图所示,整个生命周期经历了以下阶段
- 导航开始:记录
navigationStart时间点 - 重定向处理:如果存在重定向,记录
redirectStart和redirectEnd时间点 DNS查找:记录domainLookupStart和domainLookupEnd时间点TCP连接:记录connectStart和connectEnd时间点- 请求发送:记录
requestStart时间点 - 响应接收:记录
responseStart和responseEnd时间点 DOM处理:记录domLoadingdomInteractivedomContentLoadedEventStartdomContentLoadedEventEnd和domComplete时间点- 页面加载:记录
loadEventStart和loadEventEnd时间点
在不同的阶段中,用户代理 (User agents 多数情况下为 browsers)会将对应的时间点写入 window.performance.timing 和 window.performance.navigation 对象中,方便后续使用
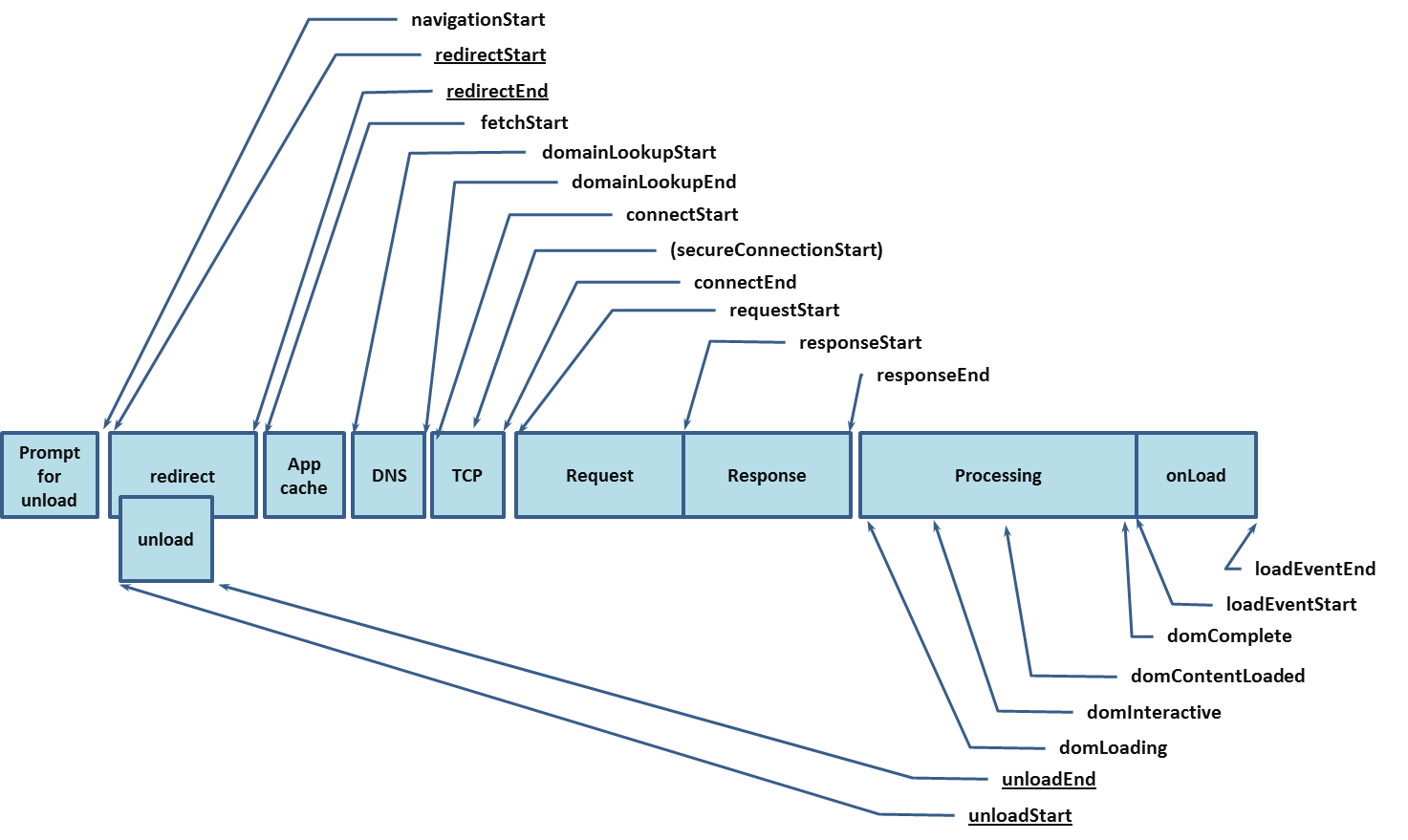
图片来源 https://www.w3.org/TR/navigation-timing/#processing-model
WARNING
- 当
window对象创建后,window.performance.timing和window.performance.navigation才能被写入 window.performance.timing和window.performance.navigation可能被浏览器禁用,此时两者的值返回null
属性
可以通过 window.performance 访问对应内容 timing 和 navigation
interface PerformanceTiming {
readonly navigationStart: number;
readonly unloadEventStart: number;
readonly unloadEventEnd: number;
readonly redirectStart: number;
readonly redirectEnd: number;
readonly fetchStart: number;
readonly domainLookupStart: number;
readonly domainLookupEnd: number;
readonly connectStart: number;
readonly connectEnd: number;
readonly secureConnectionStart: number;
readonly requestStart: number;
readonly responseStart: number;
readonly responseEnd: number;
readonly domLoading: number;
readonly domInteractive: number;
readonly domContentLoadedEventStart: number;
readonly domContentLoadedEventEnd: number;
readonly domComplete: number;
readonly loadEventStart: number;
readonly loadEventEnd: number;
}
enum NavigationType {
TYPE_NAVIGATE = 0;
TYPE_RELOAD = 1;
TYPE_BACK_FORWARD = 2;
TYPE_RESERVED = 255;
}
interface PerformanceNavigation {
readonly type: NavigationType;
readonly redirectCount: number;
};
interface Performance {
readonly timing: PerformanceTiming;
readonly navigation: PerformanceNavigation
}
interface Window {
readonly performance: Performance
}WARNING
需要注意的是 Navigation Timing 特性已被标注为废弃,并不推荐使用。但由于其良好的兼容性(Chrome 6),仍有了解的必要
Navigation Timing Level 2
目前在 W3C 议程上的是最新的 Navigation Timing Level2 标准。简而言之,该标准相对于 Navigation Timing - 2012 主要有以下改变:
- 提供了更多的时间点和属性
- 提供协议支持
使用方式与 Navigation Timing - 2012 也有所不同,可以通过 performance.getEntriesByType 或者 PerformanceObserver 获取到对应的属性
performance.getEntriesByType 支持多种类型的资源,通过指定 type 可以指定获取对应的 performance 数据
const [navigationTl] = performance.getEntriesByType("navigation");
const srcTimelines = performance.getEntriesByType("resource");需要注意的是,performance.getEntriesByType 不会通知到对应 performanceNavigationTiming 属性的变化,返回的是 FrozenArray 格式的 调用时的 performance timeline。如果需要动态监听变化,应该使用 PerformanceObserver
function perfObserver(list, observer) {
list.getEntries().forEach((entry) => {
if (entry.entryType === "mark") {
console.log(`${entry.name}'s startTime: ${entry.startTime}`);
}
if (entry.entryType === "measure") {
console.log(`${entry.name}'s duration: ${entry.duration}`);
}
});
}
const observer = new PerformanceObserver(perfObserver);
observer.observe({ entryTypes: ["measure", "mark"] });变更详情,摘自 w3c Editor's Draft
Performance interface移动到单独的 PERFORMANCE-TIMELINE-2 标准中,支持该标准- 建立在的 RESOURCE-TIMING-2 基础上
- 支持 HR-TIME-2
- 支持 [RESOURCE-HINTS] 的预渲染技术
- 暴露自上次非重定向导航以来的重定向次数
- 暴露 next hop network protocol
- 暴露
transfer以及编解码的请求体大小 - 强制
secureConnectionStart属性
Level 2 处理模型
- 导航开始:记录
startTime和navigationStart时间点 Service Worker:如果存在Service Worker,记录workerStart时间点- 重定向处理:如果存在重定向,记录
redirectStart和redirectEnd时间点,并更新redirectCount属性 DNS查找:记录domainLookupStart和domainLookupEnd时间点TCP连接:记录connectStartsecureConnectionStart(如果适用)和connectEnd时间点- 请求发送:记录
requestStart时间点 - 响应接收:记录
responseStartresponseEndtransferSizeencodedBodySize和decodedBodySize时间点 - 底层协议:记录
nextHopProtocol属性 DOM处理:记录domInteractivedomContentLoadedEventStartdomContentLoadedEventEnddomComplete时间点- 页面加载:记录
loadEventStart和loadEventEnd时间点 - 预渲染:如果存在预渲染,记录
prerenderStart和prerenderEnd时间点
对比 Navigation Timing 2012 可以发现,Navigation Timing Level2 的记录颗粒度明显更细致,并且多了诸如 Service Worker 等
属性
/** 导航类型 */
enum NavigationTimingType {
"navigate",
"reload",
"back_forward",
"prerender"
};
/** 未存储原因 */
interface NotRestoredReasons {
readonly src?: string;
readonly id?: string;
readonly name?: string;
readonly url?: string;
readonly reasons?: {reason: string}[];
readonly children?: {reason: string}[];
}
interface PerformanceNavigationTiming {
readonly unloadEventStart: number;
readonly unloadEventEnd: number;
readonly domInteractive: number;
readonly domContentLoadedEventStart: number;
readonly domContentLoadedEventEnd: number;
readonly domComplete: number;
readonly loadEventStart: number;
readonly loadEventEnd: number;
readonly type: NavigationTimingType;
readonly redirectCount: number;
readonly criticalCHRestart: number;
readonly NotRestoredReasons? notRestoredReasons?: ;
}